🏥 Improving Surgeries With AI and Robotics
AI and Robotics are helping surgeons by allowing for more precision and efficiency when performing surgeries.

Today's Highlights
- How AI and Robots are making surgeries better for the surgeon and patient
- This Week On BuzzBelow - a recap on this week's topics
- In Other News - a few interesting developments we're tracking
AI and Robotics have changed healthcare by helping to increase the efficiency and accuracy of surgery for patients. Robotics and AI have been delivering advances that improve surgical skills and change patient outcomes, from straightforward activities to intricate surgical operations.
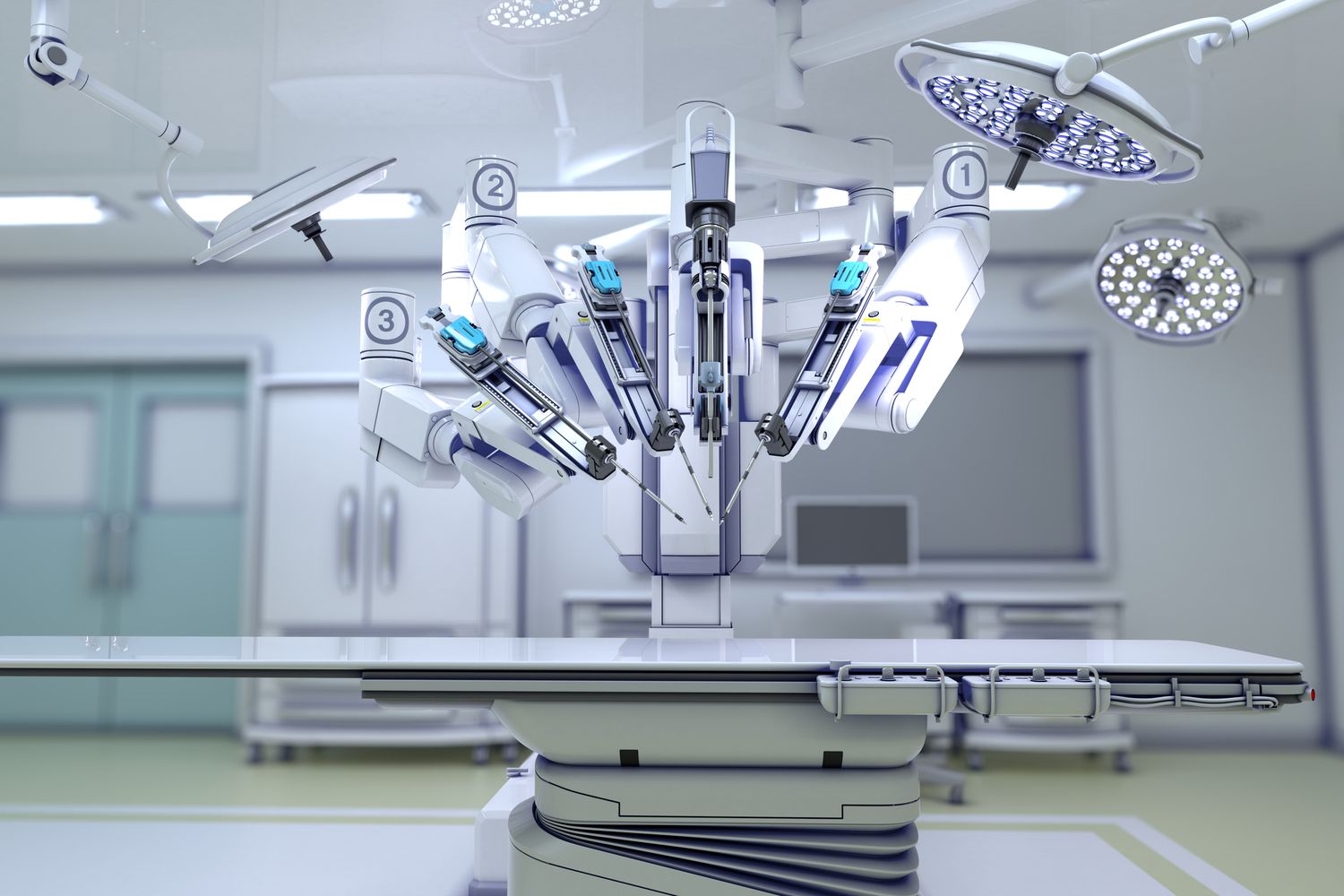
The first robotic surgery took place in the 1980s. The primary goal was to improve surgeon's capacity and surgical accuracy. Today's surgeries, including cardiac, urology, and orthopedic procedures, all benefit from the assistance of robots. Here are some ways AI enhances robotic surgery:
- Precision: Particularly in tiny procedures, robots can move with a degree of accuracy that can be difficult for the human hand.
- Flexibility: Robots offer more versatility throughout the treatment since they may access places and angles that could be challenging for a human surgeon.
- Minimized Trauma: Small incisions allow for the performance of many robot-assisted procedures, which speeds up patient recovery and reduces scarring. In fact, the conversion rate of straight-stick laparoscopy to open surgery was 25%. But with a robotic platform, the conversion rate was less than 5%, thus reducing blood loss and morbidity.
- Training: Artificial intelligence (AI) and virtual reality (VR) can imitate operations for educational reasons, giving aspiring surgeons a close-to-real experience.
- Real-time assistance: While doing the surgery, certain AI systems can direct the surgeons by providing real-time insights based on the data it analyzes.
- Imaging: With the use of AI-enhanced imaging technologies, surgeons can make diagnoses and perform procedures with more precision. Pathologists have even decreased their error-rate of recognizing cancer-positive lymph nodes from 3.4% to 0.5%.
One of the most used robot surgical systems is the Da Vinci Surgical System. The system is used in minimally invasive surgeries, and its robot arms are controlled by a surgeon while seated at a computer console. Even though this system was released in 2000, it is still used in 3 out of 4 prostate cancer surgeries in the US.
An innovative step toward the future of medical operations is the use of robotics and AI in surgery. With the current medical robotics market worth $4.7 billion and it is expected to grow another 11% by 2030, surgical procedures will undoubtedly grow more specialized, precise, and patient-focused as technology develops and merges with the medical industry. The difficulty is striking a balance between the essential human touch and knowledge that are at the core of healthcare and technology improvements.
This Week on BuzzBelow

In Other News







